Dictionary methods and operators
Updated on 28 Dec 2022
Python Dictionary comes with a slew of methods that we can use. The most common is len to return the number of elements, and str which will return a printable version of the dict.
Quick Summary
Here is a list of the more common methods that you might use with a dict,
dict.clear()-> Removes all elements of dictionary dictdict.pop(key)-> Removes the element from the dictionarydict.items()-> Returns a list of dict’s (key, value) tuple pairsdict.keys()-> Returns list of dictionary dict’s keysdict.values()-> Returns list of dictionary dict’s values
in operator
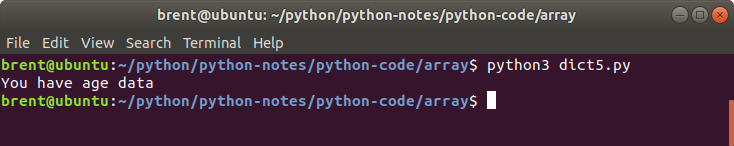
The in operator is really useful for a dictionary. It returns true or false depending on whether a key exists in the dictionary. The example below illustrates this.
myData = {
'Name': 'Zara',
'Age': 7,
'Class': 'First'
}
if 'Age' in myData:
print('You have age data')
else:
print('Age data missing')
Note you can also use the not in operator as well - to see if a key is not in a dictionary!
Dictionary - Guided Exercise
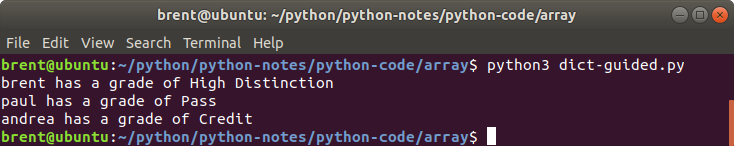
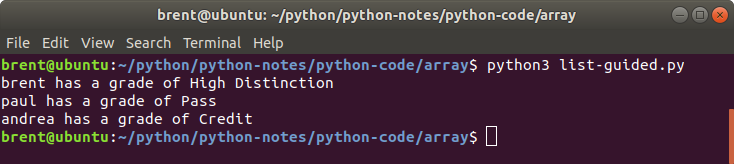
In an earlier chapter on lists we followed a guided exercise on synchronized lists.
students = ['brent', 'paul', 'andrea']
grades = ['High Distinction', 'Pass', 'Credit']
How do we get the following output?
We want to follow on from this exercise but use a combination of a dictionary and list to describe our data.
Solution
First step is figuring out what our data is and how we are going to map it. This is how I envisage the structure.
- first name and grade which can be combined into a
dictionary - a
listthat can contains many of thedictionaryabove.
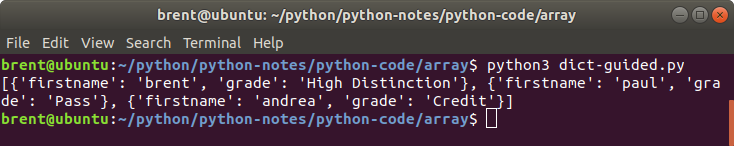
A first go will look something like this:
students = [
{
'firstname': 'brent',
'grade': 'High Distinction'
},
{
'firstname': 'paul',
'grade': 'Pass'
},
{
'firstname': 'andrea',
'grade': 'Credit'
}
]
print(students)
Looping thru a list with a dictionary
Looping thru a list with a dictionary is the same as looping thru a list with any other data type. So we can do this:
students = [
{
'firstname': 'brent',
'grade': 'High Distinction'
},
{
'firstname': 'paul',
'grade': 'Pass'
},
{
'firstname': 'andrea',
'grade': 'Credit'
}
]
for student in students:
print(student['firstname'], 'has a grade of', student['grade'])